|
|
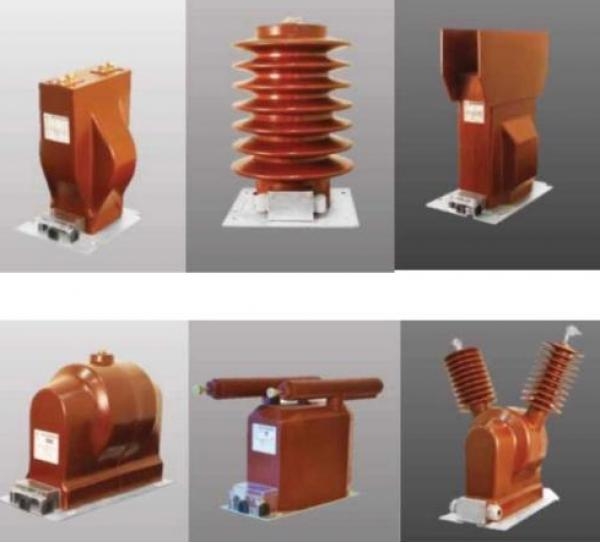 Instrument Transformers, Current and Voltage Transformers up to 36 kV
Instrument Transformers play a crucial role in electrical systems by providing accurate measurements of electrical quantities, enabling safe and efficient operation. Among these, Current Transformers (CTs) and Voltage Transformers (VTs) are essential components. CTs and VTs are often categorized based on their application, such as Metering Transformers for accurate measurements, and Protection Transformers for system protection. Power Transformers are designed to handle high voltage and are often found in substations. These transformers can be classified into High Voltage Instrument Transformers and Low Voltage Instrument Transformers, depending on the voltage levels they manage. In specific applications, Indoor Instrument Transformers are used within buildings, whereas Substation Instrument Transformers are utilized in outdoor substation environments. Medium Voltage Instrument Transformers serve systems operating within medium voltage ranges, while Dry-Type Instrument Transformers are known for their safety and reliability due to the absence of oil, reducing the risk of fire. Advanced designs include Sensor Transformers, which are typically compact and used for monitoring purposes, and Toroidal Instrument Transformers, known for their ring-shaped core, which ensures efficient magnetic coupling. Bushing Current Transformers are designed to be integrated into the bushing of a high voltage apparatus, while Ring-type Current Transformers are commonly used for retrofitting existing systems. Instrument Transformers also differ in terms of their operating principles, with Electromagnetic Instrument Transformers relying on electromagnetic induction, and Electronic Instrument Transformers using electronic circuits for signal processing. The Transformer Accuracy Class is a critical specification, ensuring that the transformers provide precise and reliable measurements, which is essential for both metering and protection purposes.
|